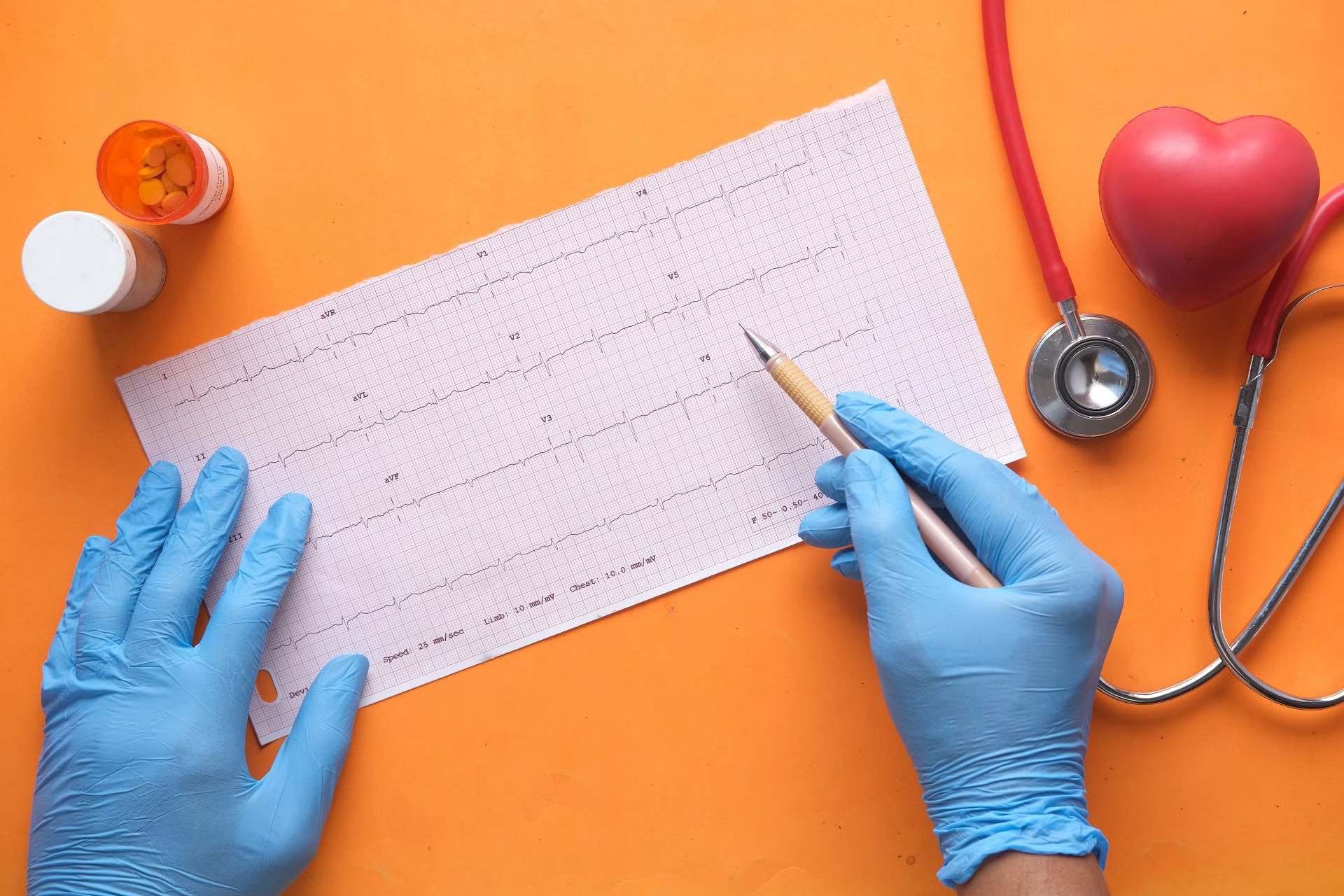
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a test to record the electrical signals in the heart. It shows how the heart is beating. Sticky patches called electrodes are placed on the chest and sometimes on the arms or leg
If the test is normal, it should show that your heart is beating at an even rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute. Many different heart conditions can show up on an ECG, including a fast, slow, or abnormal heart rhythm, a heart defect, coronary artery disease, heart valve disease, or an enlarged heart.
What Abnormal Results Mean. Abnormal ECG results may be a sign of: Damage or changes to the heart muscle. Changes in the amount of the electrolytes (such as potassium and calcium) in the blood.
Stress can trigger both atrial and ventricular arrhythmias. Evaluating ECG signatures of stress can provide mechanistic information, as well as serving as surrogate endpoints for studies investigating therapeutic approaches.